Seeing infrared: scientists create contact lenses that grant ‘super-vision’ | Science
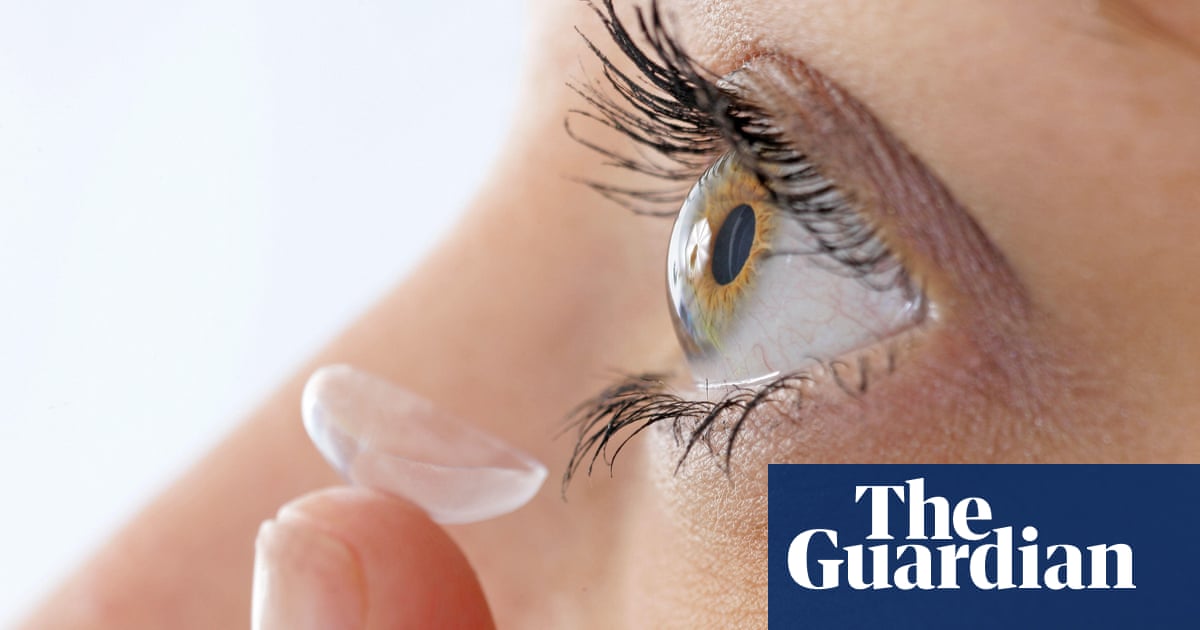
The researchers gave people the taste of supernatural vision after creating lenses that allow them to see the infrared light, a group of invisible electromagnetic spectrum of the naked eye.
Unlike night vision glasses, contact lenses do not need any source of energy, and because they are transparent, the younger can see infrared and all regular light -visual colors at the same time.
Professor Tian Xue, a neuroscientist at the University of Science and Technology in China, said that work paved the way for a set of contact lenses, glasses and other devices that can be worn and that gives people a “super vision”. He added that this technology can help people who suffer from color.
The lenses are the latest penetration led by the team’s desire to expand human vision beyond its narrow natural scope. The wavelengths of light that humans can see forms less than a hundred percent of the electromagnetic spectrum.
“More than half of the solar radiation energy, which is like infrared light, remains imperceptible to humans,” said Dr. Yukian Ma, a project researcher.
The rainbow extends from the visible colors of humans the wavelengths from 400 to 700 nm (is a million of millimeters). But many other animals feel the world differently. Birds, bees, ringtone and mice can see ultraviolet light, and very short wavelengths so that humans cannot realize. Meanwhile, some snakes and vampires have organs that discover infrared, or thermal radiation, which helps them search for prey.
To expand the scope of human vision and enhance our experience in the world, scientists have developed the so -called nanoparticles. The molecules absorb light infrared and re -emission as visible light. For study, scientists have chosen molecules that absorb the light of infrared, which includes very long wavelengths for humans to perceive and turn them into red, green or visible blue light.
in Previous workThe research team gave mice near infrared by injecting the nanoparticles under the retina under the retina, the light membrane of the light at the back of the eye. But they noticed that this “may not be easily accepted by humans,” they looked for a lesser -e -strategy.
Writing in cell magazineScientists describe how they made soft adhesive lenses with transformational nanoparticles. When wearing it, people can see signals similar to the Morse symbol from the LED infrared index and told the direction from which the light came with infrared.
Her vision of infrared improved when their eyes were closed, because the eyelids prevent visible light more than infrared, so there was a less clear light for intervention.
The lenses are not sensitive enough to see normal low levels of infrared light, and because warm things are often radiated in infrared, lenses do not provide a thermal vision. Scientists say future work will focus on making the most effective lenses.
Xue said: “If scientists can develop high -efficiency nanoparticles, it may be possible to see the surrounding infrared light with contact lenses,” Xue said.
Even without a full infrared vision, Xue sees applications. For example, the secret messages sent by infrared will not only be visible to people who wear contact lenses.
A similar approach to people who suffer from color may help by converting wavelengths that they cannot see in the shapes they can.



